Polymaker
Polymaker PC-ABS 1kg 1.75mm Filament
Polymaker PC-ABS 1kg 1.75mm Filament
Out of stock
Couldn't load pickup availability
High quality PC/ABS polymer blend based on a specialty Coversto Bayblend® material well suited for automotive applications and metalling.
- High quality Polymaker PC-ABS.
- Excellent impact strength and durability.
- High heat resistance up to 111.7℃ HDT.
- Good surface adhesion for metallisation / electroless plating.
- Excellent bonding painting and welding possibilities.
- Consistent colour and tolerance (1.75mm diameter +/- 0.03mm)

Polymaker™ PC-ABS is a PC/ABS polymer blend which offers excellent toughness and heat resistance while displaying a good surface finish and good compatibility with metal plating. Polymaker™ PC-ABS is based on a specialty blend well suited for metallising. Polymaker™ PC-ABS can be metalled by deposition of a metallic layer in a high vacuum or by electroless plating. The post-processing characteristics and heat resistance of Polymaker™ PC-ABS make it an ideal material for automotive interior parts such as dashboard, door handles or instrument panels alongside general purpose prototyping and manufacturing applications.
Features
- Excellent Toughness - Polymaker™ PC-ABS is a durable material offering excellent toughness and impact strength while combining the heat resistance of PC with the flexibility of ABS. Polymaker™ PC-ABS is an ideal material for a range of engineering and industrial applications and is a popular choice for automotive parts, functional prototyping, and industrial applications requiring heat resistance & impact resistance.
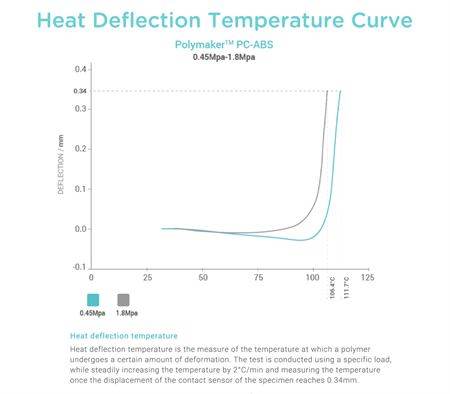
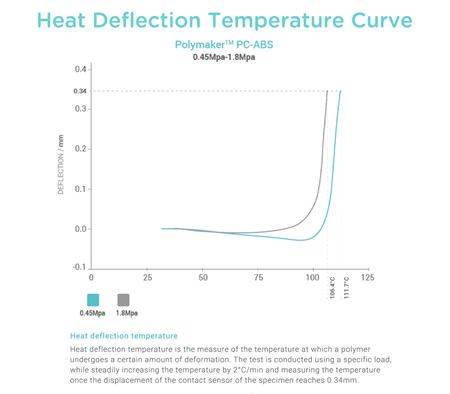
- Heat Resistant - Polymaker™ PC-ABS offers great heat resistance with a heat deflection temperature up to 111.7℃ (0.45MPa), well suited for a wide range of automotive and engineering applications.
- Good Surface Finish - Polymaker™ PC-ABS renders parts with a good surface finish and displays good surface adhesion which makes it easier to post process. Polymaker™ PC-ABS is well-suited for painting. bonding and specialized for surface finishings, i.e. by electroless plating and metallisation. Proper preparation of the surface is important for the metallising process but Polymaker™ PC-ABS can be metallised by deposition of a metallic layer in a high vacuum or by electroless plating. In the metal deposition process, the best adhesion is achieved with aluminum, tin and copper. As protection for the very thin layer of metal, a coating of paint on the molding is recommended. In the case of electroless plating, Polymaker™ PC-ABS offers the best adhesion for the electroless plating for its first layer.
- Bonding & Welding - Polymaker™ PC-ABS parts can be joined together by ultrasonic, vibration, friction, hot plate or laser welding. Polymaker™ PC-ABS parts can be bonded not only to one another, but also to other materials. This is possible using suitable adhesive glues or diffusion adhesive. In the case of adhesive glues, two-component adhesives based on epoxy and silicone resins and polyurethanes have proved excellent.
- Formulated For 3D Printing - Using Covestro’s Bayblend® family as its base material, Polymaker™ PC-ABS is specifically engineered for 3D printing to combine excellent mechanical properties and printing quality. Bayblend® is a commonly used plastic in the automotive and information technology industry. Enclosure and 90°C heated bed required; a heated chamber is highly recommended.
Printing Settings
| Nozzle Temperature | 250°C - 270°C |
|---|---|
| Build Plate Temperature | 90°C - 105°C |
| Build Surface Material | Works well with most build surfaces i.e Glass, BuildTak® etc Rigid build plates recommended compared to magnetic flex plates though this does depend on bed magnetism. |
| Build Surface Treatment | Apply Magigoo PC or PVA glue to the build surface to improve adhesion. |
| Enclosure | Highly recommended. |
| Heated Chamber | Highly recommended, 90˚C - 100 ˚C required for some geometries. |
| Cooling Fan | OFF for most printers. LOW FAN speed may be required inside some heated chambers. |
| Printing Speed | 30 mm/s - 50 mm/s |
| Retraction | The ideal retraction settings vary from printer to printer and depend on the hot end. The following settings have been a good starting point for many machines. Direct Drive: Retraction distance of 1mm with retraction speed of 20mm/s Bowden: Retraction distance of 3mm with retraction speed of 40mm/s |
| Recommended Support Material |
Self-support. |
The above are printing recommendations based on 0.4 mm nozzle. Please note ideal printing conditions may vary depending on your 3D printer setup. For high speed 3D printers, make sure to increase your extrusion temperature in order to use higher printing speeds.
PC-ABS requires a stable and hot printing environment. Before printing we recommend to pre-heat your build plate 20 - 30 minutes before printing. In colder climates a longer pre-heating time may be useful. For users printing without an actively heated chamber, be mindful of the part size and infil density, larger or denser parts will use more material which will result in more residual stresses within your part.
For other tips printing Polymaker™ PC-ABS contact us!
Annealing PC-ABS
For the best mechanical performance it is recommended to anneal parts printed in Polymaker™ PC-ABS. Annealing is the process of heating up the printed parts at a certain temperature for a certain period of time. The purpose of annealing Polymaker™ PC-ABS is to release the internal stress which accumulates during the printing process. If not annealed soon after the printing process, internal stress can create micro cracks over time and weaken the part.
Annealing Settings - 90˚C for 2 hours.
Specification
| Net Weight | 1kg |
|---|---|
| Material Type | PC-ABS |
| Density | 1.1 (g/cm3 at 21.5˚C) |
| Colour |
Black |
Compatibility
Polymaker™ PC-ABS has been engineered with 3D printing in mind however please note this material requires a heated bed and enclosure. C-ABS is a blend of PolyCarbonate and ABS, the ideal printing settings and requirements of different PC-ABS blends can vary. We highly recommend printing with an actively heated chamber for the best printing results.
Of course with thousands of unique 3d printer models on the market, we can't guarantee each filament type will work with every 3D printer. Slicer experience and setting adjustment is always required to get the most out of a material. Before jumping into an ambitious project we always recommend printing some known calibration tests to build or make adjustments to the filament profile.
Technical Data
All testing specimens were printed under the following conditions: Nozzle Temperature = 260˚C, build plate temperature = 110˚C, infil = 100%, cooling fan = OFF
All specimens were conditioned at room temperature for 24h prior to testing.
THERMAL PROPERTIES
| Value | Testing Method | |
| Glass Transition | 109°C | DSC, 10°C/min |
| Heat Deflection Temperature |
0.45MPa - 111.7°C HDT Curve |
ISO 75 |
| Vicat Softening Temperature | 135°C | ISO 306, GB/T 1633 |
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
| Value | Testing Method | |
| Youngs Modulus (X-Y) |
1,880.0 MPa | ISO 527, GB/T 1040 |
| Tensile Strength (X-Y) |
36.9 MPa | ISO 527, GB/T 1040 |
| Tensile Strength (Z) | 27.5 MPa | ISO 527, GB/T 1040 |
| Elongation at break (X-Y) | 6.2% | ISO 527, GB/T 1040 |
| Bending Modulus (X-Y) | 1,939.9 MPa | ISO 178, GB/T 9341 |
| Bending Strength (X-Y) |
60.6 MPa | ISO 178, GB/T 9341 |
| Charpy Impact Strength (X-Y) |
15.5 kJ/m2 | ISO 179, GB/T 1043 |
| Low Temperature Impact Strength (X-Y) | 11.5 kJ/m2 | ISO 179-1/1eA:2010, -30°C |
We have full MDS and technical data sheets for Polymaker™ PC-ABS and all other Polymaker products. Contact us to enquire!
The typical values presented in Polymakers data sheet are intended for reference and comparison purposes only. Due to the nature of 3D printing they should not be used for design specifications or quality control purposes.
STORAGE & DRYING
All plastics are hygroscopic meaning they absorb moisture from the air which can affect printing quality and strength of printed parts. How quickly this absorption occurs depends on the material and your environment. Polymakers PC-ABS filaments are dried and packaged in a vacuum sealed bag with desiccant to ensure the best printing quality. When not in use Polymaker PC-ABS should be stored away from sunlight and sealed in the packaged resealable bag.
Although filaments can be dried, drying will speed up the aging process of the plastic making it more brittle over time. Preventing the filament from absorbing moisture in the first place is the best solution to keep your filament working to its maximum potential. For long term storage we highly recommend storing in a sealed container with dry desiccant that reduces the relative humidity to 10-20% RH.
In-house we manage our fialments with Polymakers PolyDryer™ which keep offers best-in-class sealing to protect filaments from absorbing moisture
If you hear popping sounds and notice that the surface quality of your print is uneven or the colour is not consistent, this is a likely indicator that the filament has absorbed too much moisture. Spools of Polymaker™ PC-ABS can be dried with Polymaker PolyDryer™ using power level 3. Alternatively if you have a convection oven that is accurate at low temperatures, users can dry filament in a preheated convection oven at 75˚C for up to 6 hours. Results may vary depending on the accuracy of your oven so please be conservative. For more information about filament drying please read our user guide.
FAQ
Q: Polymaker manufacture many different PC filaments, which one should I purchase?
A: PolyLite™ PC and PolyMax™ PC are the best choices for users who are interested in 3D printing strong PolyCarbonate parts that don’t have a specialised requirement. These two materials are easier to print when compared to PC filaments from other brands. PolyLite™ PC offers transparency and the best value for general purpose printing and PolyMax™ PC is our most popular PC filament, with boosted toughness and additional benefits in printability. Aside from variances in price and mechanical performance, Polymaker™ PC-ABS, Polymaker™ PC-PBT and PolyMax™ PC-FR offer unique solutions for industrial applications, with excellent mechanical performance and higher printing requirements. Polymaker™ PC-PBT for example offers excellent toughness at subzero temperatures whereas PolyMax™ PC-FR offers the best flame retardancy. To discuss which material is the best for your printer and application, contact us today!
Q: Do I require an actively heated chamber to print PC-ABS?
A: Ideally, yes. Compared to PC and ABS filaments, PC-ABS has higher environmental temperature requirements. Success can be found printing small parts without an actively heated chamber but certainly a control chamber temperature up to 100℃ will be critical to print many geometries accurately. A higher heated chamber temperature helps to prevent the accumulation of residual stresses in your print which can reduce the effects of warping.
Q: Is it possible to print PC-ABS without warping?
A: A stable actively heated chamber high temperature environment is required to print larger PC-ABS parts without warping and whether a part is susceptible to warping will vary on how the residual stress releases within the parts geometry. Most users print PC-ABS with the heated bed set to 100˚C and an enclosed heated chamber to heat the surrounding environment; this effectively reduces internal stress which cause PC-ABS to warp or crack. To guarantee that PC-ABS can be printed at any size without warping, 3D printing with a professionally designed heated chamber is required.
Q: What is an actively heated chamber and passively heated chamber?
A: An "actively heated chamber" is an industrial printer that uses active heating elements to reach a stable and high temperature build volume. Some are designed to reach 100°C and others designed to reach up to 200°C. To extrude reliably at these temperatures and prevent thermal creep, manufacturers generally implement a bellows system or water cooling for the print head and extruder. To maximise printer up-time, the motion system is usually designed to ensure core electronics and stepper motors sit outside of the heated environment. A "passively heated chamber" is a marketing term that is sometimes used to describe a printer with a heated build plate and an enclosure. The heated build plate will radiate heat and the enclosure traps this heat but the internal temperature will generally sit between 40 and 60℃. A passively heated chamber is useful but there will be significantly more limitations in comparison to using an actively heated chamber.
Q: Is annealing Polymaker PC-ABS required?
A: We recommend annealing all models printed in Polymaker™ PC-ABS right after the printing process to release the residual internal stress in your parts. Annealing is an important process release these stresses which will maximise the mechanical properties of your part and ensure they aren't compromised. If left within a part, residual stresses can result in microscopic stress cracking which will ultimately effect the mechanical properties of your part. The hotter your printing environment, the less residual stresses will likely be in your part, the colder your printing environment, the more residual stress will have accumulated in your part. In simple terms printing parts in PC-ABS without an actively heated chamber, or potentially without any enclosure may be possible for some applications but annealing is highly recommended to ensure the best mechanical properties. Users who print with an actively heated environment will have significantly less residual stress in their parts, we still recommend annealing but the mechanical effects of micro-cracking are inherently lessened due to the reduction in stresses. We recommend annealing parts in an oven for 2 hours at 90˚C.
Q: Can I remove the layer lines from Polymaker™ PC-ABS?
A: Layer-lines are an inherent feature of FDM / FFF 3D printing. Polymaker™ PC-ABS can be smoothed and post-processed in a multitude of ways including sanding or tumbling. If you plan to sand the print, it would be better to print at least 3 perimeters/shells or create a minimum wall thickness of 1.2mm. Tumbling is a post-processing technique for smoothing and polishing the surfaces of objects automatically. Polymaker™ PC-ABS is a suitable candidate for vibrational tumbling due to its mechanical strength and impact resistance as the nature of the tumbling process involves thousands of surface impacts with cutting and polishing stones. The process duration is decided by many factors including the kind of grit, the size and power of the machine and the material of polished parts. Tumbling offers an effective solution that is holistic and fully automated and less aggressive that hand sanding. Compared to sanding, vibrational tumbling does have its drawbacks, as only the parts that come in contact with the stones will be sanded which means fine details or hard to reach areas will not be affected whilst the outside, easily reached areas may become over polished.
Q: Can I metallize Polymaker™ PC-ABS?
A: Polymaker™ PC-ABS is a specialty blend well suited for metallising. Polymaker™ PC-ABS can be metallized by deposition of a metallic layer in a high vacuum or by electroless plating. In the metal deposition process, the best adhesion is achieved with aluminum, tin and copper. As protection for the very thin layer of metal, a coating of paint on the molding is recommended. In the case of electroless plating, Polymaker™ PC-ABS offers the best adhesion for the electroless plating for its first layer. Proper preparation of the surface is important for the metallizing process.
Q: Can I paint Polymaker™ PC-ABS?
A: Polymaker™ PC-ABS is well-suited for painting. To ensure a good paint finish, the surfaces must be clean (free of dust or grease). Particularly good adhesion can be achieved using polyurethane-based paint. It is recommended to contact the paint manufacturer prior to painting as some combinations of solvents are unsuitable for the PC-ABS blend and can cause defects or stress cracking.
Q: Can I weld Polymaker™ PC-ABS?
A: Polymaker™ PC-ABS parts can be joined together by ultrasonic, vibration, friction, hot plate or laser welding. In order to achieve the best possible component quality when using ultrasonic welding, it is important to ensure a correctly formed weld seam.
Q: How else can I bond Polymaker™ PC-ABS?
A: Polymaker™ PC-ABS parts can be bonded not only to one another, but also to other materials. This is possible using suitable adhesive glues or diffusion adhesives. Drycleaning fluid or similar cleaning agents, which do not damage the material, can be used to remove grease. Roughening and subsequently cleaning the surfaces can also improve glue adhesion. In the case of adhesive glues, can also improve two-component adhesives based on epoxy and, silicone resins and polyurethanes.
Q: Is Polymaker™ PC-ABS UV resistant?
A: We currently have no data in relation to UV resistance. For applications that won't be post-processed and require good UV resistance we recommend considering PolyLite™ ASA.
Q: Should I rewind this filament if I want to use it with a different spool?
A: We strongly advise against tampering with the product by rewinding. See our article for full details about the risks. All Polymaker filaments are wound with tension but without strain. Rewinding completely rearranges the curvature of the winding and this strain over time can cause most plastics to catastrophically break. If for some reason your printer is locked into fitting less than standard sized spools, there may be safe printable adaptors or external mounting solutions available.
Don't know where to start? Or which filament will suit your application? We have a broad range of support options including telephone support. Contact us today!
| Filament | |
| Diameter | 1.75mm |
| Spool Weight | 1kg |
Polymaker™ PC-ABS is a blend of two of the most popular 3D printing materials on the market, Polycarbonate and ABS. The advantages of this blend are high impact, heat resistance and easy processability. The polycarbonate boosts the heat resistance and toughness of the material while the ABS contributes to the good processing properties.
- Specialised for processing & surface finishings
- Excellent toughness.
- Excellent heat resistance.
- Fantastic tensile strength, flow and inter-layer adhesion.
- Improved flexibility similar to ABS.
- Based off Covestro's Bayblend® resins, Polymaker™ PC-ABS has been engineered and optimised specifically for 3D printing.
Polymaker™ PC-ABS is well suited for tooling, functional prototyping, automotive and manufacturing applications requiring high impact resistance. Polymaker™ PC-ABS uses Covestro’s Bayblend® family as its base material which is a commonly used plastic in the automotive and information technology industry today. Polymakers partnership with Covestro has brought new 3D printing filaments to the market by taking formulas that are already well known to industry professionals and optimising them for 3D printing. Polymaker™ PC-ABS is an ideal material for automotive interior parts such as dashboard, door handles or instrumental panel and is a material with good surface adhesion which makes it easier to post process and meet todays industry standards.
Polymaker™ PC-ABS parts can be joined together by ultrasonic, vibration, friction, hot plate or laser welding. Polymaker™ PC-ABS parts can be bonded not only to one another, but also to other materials. This is possible using suitable adhesive glues or diffusion adhesive. In the case of adhesive glues, two-component adhesives based on epoxy and silicone resins and polyurethanes have proved excellent.

Mirror housing 3D printed in Polymaker™ PC-ABS offers excellent processability!
Polymaker™ PC-ABS is well-suited for painting and post-processing and can be metallised by deposition of a metallic layer in a high vacuum or by electroless plating. In the metal deposition process, the best adhesion is achieved with aluminium, tin and copper. As protection for the very thin layer of metal, a coating of paint on the moulding is recommended. In the case of electroplating, Polymaker™ PC-ABS offers the best adhesion for the electroless plating for its first layer.
Materials
Materials
PLA - This solid filament is used to make models that are a refined representation with rigid properties.
TPU - This flexible filament holds the shape of the model and can with stand being twisted and squashed to survive the field environment.
Shipping
Shipping
Free standard shipping and Express for free orders over $300 calculated at the checkout.
All items are shipped from Townsville, QLD.
Shipping World Wide - coming soon.
Care Instructions
Care Instructions
PLA
Temperature:
Keep it cool! PLA starts to soften at around 60°C (140°F), so avoid placing it near heat sources or leaving it in hot cars.
Sunlight:
Prolonged direct sunlight can cause fading and potential deformation. Try to keep it out of long sun exposures.
Cleaning:
Gently wash with warm water and a bit of mild soap using a soft cloth. No harsh scrubbing, please!
Handling:
Handle with care—avoid excessive bending or dropping it, as PLA is rigid and can crack or break.
Storage:
Store in a cool, dry place to maintain its shape and longevity.
TPU
Temperature:
TPU is built to be flexible, but still avoid extreme or prolonged heat. It’s more resilient than PLA, but unnecessary heat can still degrade it over time.
Sunlight:
Try not to leave TPU items in direct sunlight for too long, as UV rays can fade the colors and slowly affect the material quality.
Cleaning:
Just like PLA, a quick clean with warm water and mild soap works great. Use a soft cloth and don’t be too rough.
Handling:
Enjoy its flexibility! However, even though TPU can bend, continuous stretching or heavy impacts might wear it out faster.
Storage:
Keep it in a cool, dry spot away from harsh elements to maintain its flexibility and appearance.
Share